Depth First Search Chinese version address
Depth First Search
Overview
Depth first search of the graph is similar to the preorder traversal of the tree.
Suppose that the initial state is that all the vertices in the graph are not accessed, then starting from a vertex and first access to it, nextly, the depth first search traversal from each of its non-accessed adjacency points in turn, until all the vertices that have a path to the starting vertex in the graph are accessed. If there are other vertices that are not accessed, then choose another unvisited vertex as a starting point, repeat the above process until all graph vertices have been visited.
Diagram
Depth first search for undirected graphs
The following is an example of undirected graph, to demonstrate the depth first search.

Depth first search of the graph above, starting with vertex A:
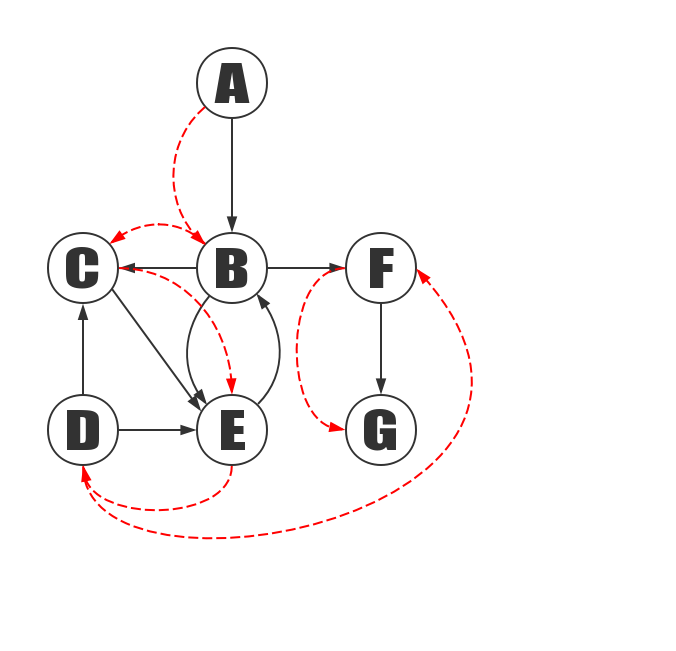
Steps:
- Access to A.
- Access to C. Because the vertices A,B,C,D,E,F,G are stored in order in this paper, C is in front of D and F, so visit C first.
- Access to B. Because B before D, first visit B.
- Access to D. After having visited C’s adjacency point B at step 3, B has no unvisit adjacency points, thus, it returns to another adjacency point D that accesses C.
- Access to F. All adjacency point of B and C are accessed, so return to A and access to next adjaceny point of A.
- Access to G.
- Access to E.
C++ Implememtation
Adjacency Matrix Version
1 | // Work in progress |
Adjacency List Version
1 | // Work in progress |
Depth first search for directed graphs
The following is an example of directed graph, to demonstrate the depth first search.
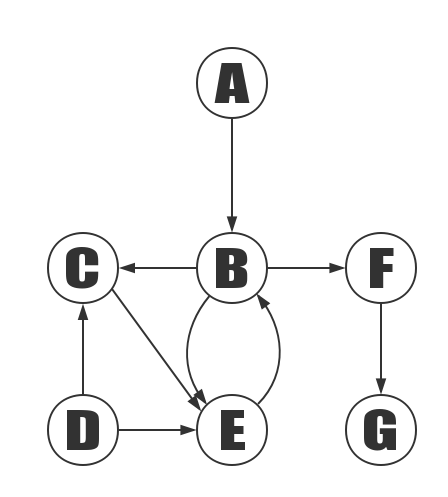
Depth first search of the graph above, starting with vertex A:

Steps:
- Access to A.
- Access to B. After visiting A, the next vertex to which A should go is the vertex B that should be accessed next.
- Access to C. After visiting B, what should be followed is another vertex of B’s out-edge. Because C is the first one, so first visit it
- Access to E. Next to the other vertex of the out-edge of the C vertex.
- Access to D. Then visit the other vertices of E’s out edge, vertices B and D. Vertex B has already been visited, so visit vertex D.
- Access to F.
- Access to G.
C++ Implememtation
Adjacency Matrix Version
1 | // Work in progress |
Adjacency List Version
1 | // Work in progress |