RedBlackTree III Chinese version address
Basic operation of red black trees
Delete
The method of deleting a node is the same as that of deleting a node in a binary search tree.
Binary search tree Delete pseudo code
1 | TREE-DELETE(T, z) |
According to the node to be deleted according to the number of sons can be divided into three cases
- No child nodes. just set the child node of the parent node to NULL and delete the child node.
- Only one child node, the parent node’s child node pointer points to the grandson node, delete the son node.
- Two child nodes, After deleting the node, but also to ensure that the search binary tree structure. In this case, the largest element in the left child node or the smallest element in the right child node can be placed in the position of the node to be deleted to ensure the structure is unchanged.
Binary search tree Delete pseudo code
1 | RB-DELETE(T, z) |
After you delete a node, it may violate the feature of the red black tree.
- If you delete the red node, then the feature of red black tree remains. At this time do not do the correction operation.
- If the deleted node is a black node, the feature of the red black tree may be changed, and we want to make corrections to it
So what are the feature of trees that will change?
- If the delete node is not the only node in the tree, then the number of black nodes to each leaf node of the delete node will change, and the property 5 is destroyed.
- If the deleted node’s only non-empty child node is red, and the deleted node’s parent node is also red, then the feature of 4 is destroyed.
- If the deleted node is the root node and its only non-empty child node is red, the new root node will be red after deletion, violating property 2.
The above repair looks a bit complicated, here we use an analytical skills:
begin to adjust the node from which the node was removed later, And think it has an extra black color. What is the meaning of an extra black here? We do not add the nodes of the red and black trees to another color of red and black. Here is just an assumption, and we think we are currently pointing to it, so there is an extra black. It can be thought that its black color is inherited from its parent after it was deleted. It can now hold two colors. If it was originally red, then it is red + black, and if it is black then its current color It is black + black. With this extra black, the feature of red-black tree 5 will remain unchanged. Now it is enough to resume other things as far as possible, and try to move all the possibilities to the root as far as possible.
If it is the case, the recovery is relatively simple:
The current node is red + black.
The current node is set to black, the end of the red-black tree at this time the nature of all recovery.
The current node is black + black and is the root node.
do nothing, the end.
But the following situation, it will be more complicated
| Case | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | The current node is black + black and the sibling node is red (in this case, the children of the parent node and sibling nodes are divided into black). |
| 2 | The current node is black and black and the brother is black and both siblings have black children. |
| 3 | The current node color is black + black, brother node is black, brother’s left child is red, the right child is black. |
| 4 | The current node color is black-black, its sibling node is black, but the sibling node’s right child is red, the sibling node’s left child’s color is arbitrary |
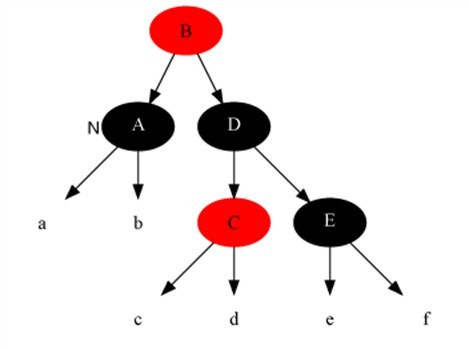
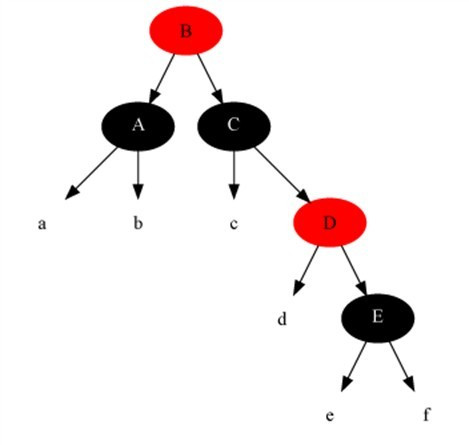
Case Description
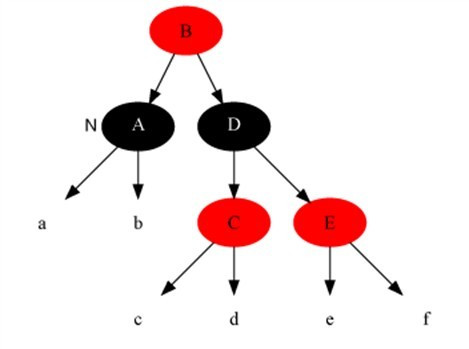
Case 1
Description
The current node is black + black and the sibling node is red (in this case, the children of the parent node and sibling nodes are divided into black).
Method
- Set the parent node to red.
- Set the brother nodes to black.
- Do left rotation on parent node.
- reset the brother nodes.
pseudo code
1 | while x ≠ root[T] and color[x] = BLACK |
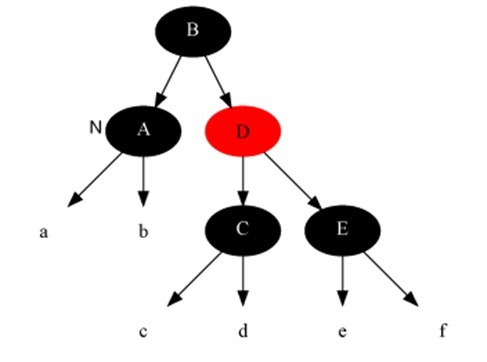
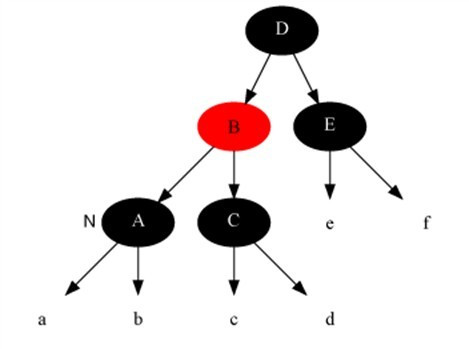
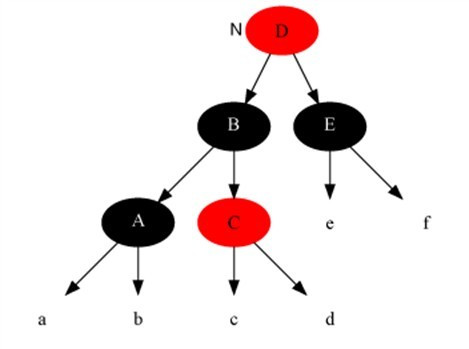
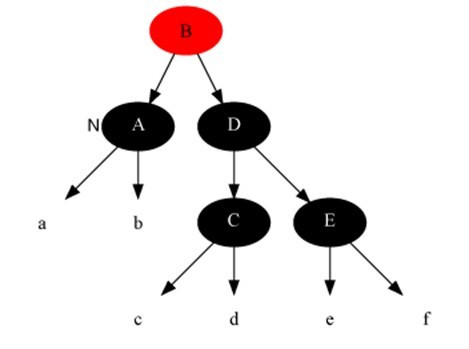
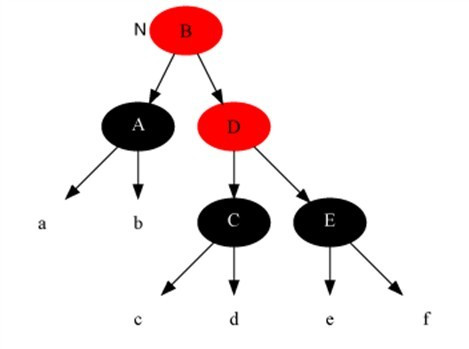
Case 2
Description
The current node is black and black and the brother is black and both siblings have black children.
Method
- Set brother node to red.
- Set current node to parent node.
pseudo code
1 | if color[left[w]] = BLACK and color[right[w]] = BLACK |
Case 3
Description
The current node color is black + black, brother node is black, brother’s left child is red, the right child is black.
Method
- Set brother node’s left child node to black.
- Set brother node to red.
- Do right rotation on brother node.
- reset brother node.
pseudo code
1 | else if color[right[w]] = BLACK |
Case 4
Description
The current node color is black-black, its sibling node is black, but the sibling node’s right child is red, the sibling node’s left child’s color is arbitrary
Method
- Set the brother node to the color of parent node.
- Set parent node to black.
- Set the brother node’s right left node to black.
- Do right rotation on parent node.
- set current node to root node.
pseudo code
1 | color[w] ← color[p[x]] ▹ Case 4 |